Features in OpenEdgeE11 and Above
- Rajesh S Nair

- May 15, 2018
- 2 min read
1.OpenEdge Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
By providing application transparent data encryption, TDE provides both security and performance needs using standard encryption libraries and encryption key management for secure, encrypted data supporting several encryption ciphers (AES, DES, DES-3 & RC4).
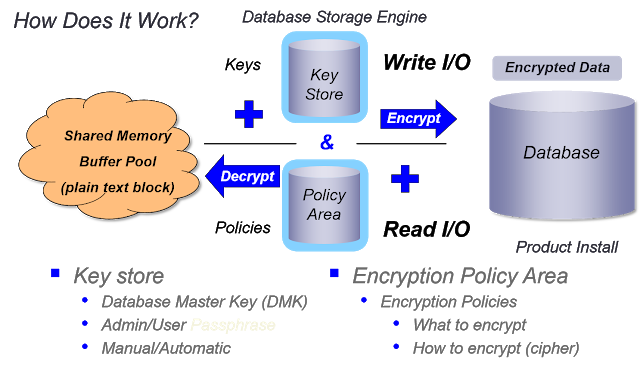
Major Encryption features are as below :
>Encrypted backup/restore>Optionally encrypt binary data dump>Encrypt data over time or immediately>No application changes>Full index capabilities on encrypted data
Supporting utilities:>Enable/disable>Epolicy manage <area | table> rekey | update | encrypt>Epolicy scanTable/index move w/possible re-encryptionWe can also change encryption policies online.
2.Multi-Tenant Database
A multi-tenant OpenEdge database is a shared database with a shared schema and logically and physically isolated data storage on a per tenant or group basis. Each object (table, index, LOB) is stored in a partition. Partitions keep data physically separate for each tenant. Partitions can exist in the same storage area or different storage areas.
It enables to develop multi-tenant applications by building multi tenant tables into the database.
The tenants would share the same schema definition.The data in the database is physically partitioned by tenant identity.
For tables that are defined to be multi-tenant, each tenant has its own instance of the multi-tenant table (unless a partition for that table has not been allocated for that tenant). Tenants have access only to the data in the instances designated for that specific tenant as well as to tables that are shared.
To enable an OpenEdge database for multi-tenancy from the command line, use the proutil command with the ENABLEMULTITENANCY qualifier. For example:
proutil <dbname> -C enablemultitenancy
To programmatically enable an OpenEdge database for multi-tenancy, use OS-COMMAND statement. For example:
DEFINE VARIABLE cCommandLine AS CHARACTER NO-UNDO.
ASSIGN
cCommandLine = "proutil sportsmt -C enablemultitenancy".
OS-COMMAND SILENT VALUE(cCommandLine).
To check whether an OpenEdge database is enabled for multi-tenancy or not, use the IS-DB-MULTI-TENANT function. For example:
MESSAGE IS-DB-MULTI-TENANT("sportsmt")
VIEW-AS ALERT-BOX INFO BUTTONS OK.
To check whether an OpenEdge database table is multi-tenant table, use the IS-MULTI-TENANT attribute of its buffer object handle. For example:
MESSAGE BUFFER Customer:HANDLE:IS-MULTI-TENANT
VIEW-AS ALERT-BOX INFO BUTTONS OK.
3.Utility Enhancements
Roll forwardrfutil <db> -C roll forward –ailist <ailist- name>Can now specify a list of files to roll forward rather than individual onesAvoids redo on each restartAlso per file completion status info provided
dbrestrictRestricts access to the database for processes other than thespecified operation
proutil <db> -C dbrestrict [ datamove | rollforward ] [ enable | disable | status]
Unlike “oplock”, allows access by certain read-only activities andprostrct addFor “datamove” allows DB Broker, promon & proshut
Prorest can enable –dbrestrict too!




Comments